Azure Database Connection Guide
Overview
This guide covers how to configure and connect to Azure Database services (MySQL and PostgreSQL).
Setting Up Azure Database
Creating a New Database Server
- Log into the Azure Portal
- Navigate to "Azure services" section
- Select either:
- "Azure Database for MySQL servers" for MySQL databases
- "Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers" for PostgreSQL databases
- Or use the search bar at the top to find these services
PostgreSQL CDC Mode Configuration
For PostgreSQL CDC mode, two additional steps are required:
Enable logical replication
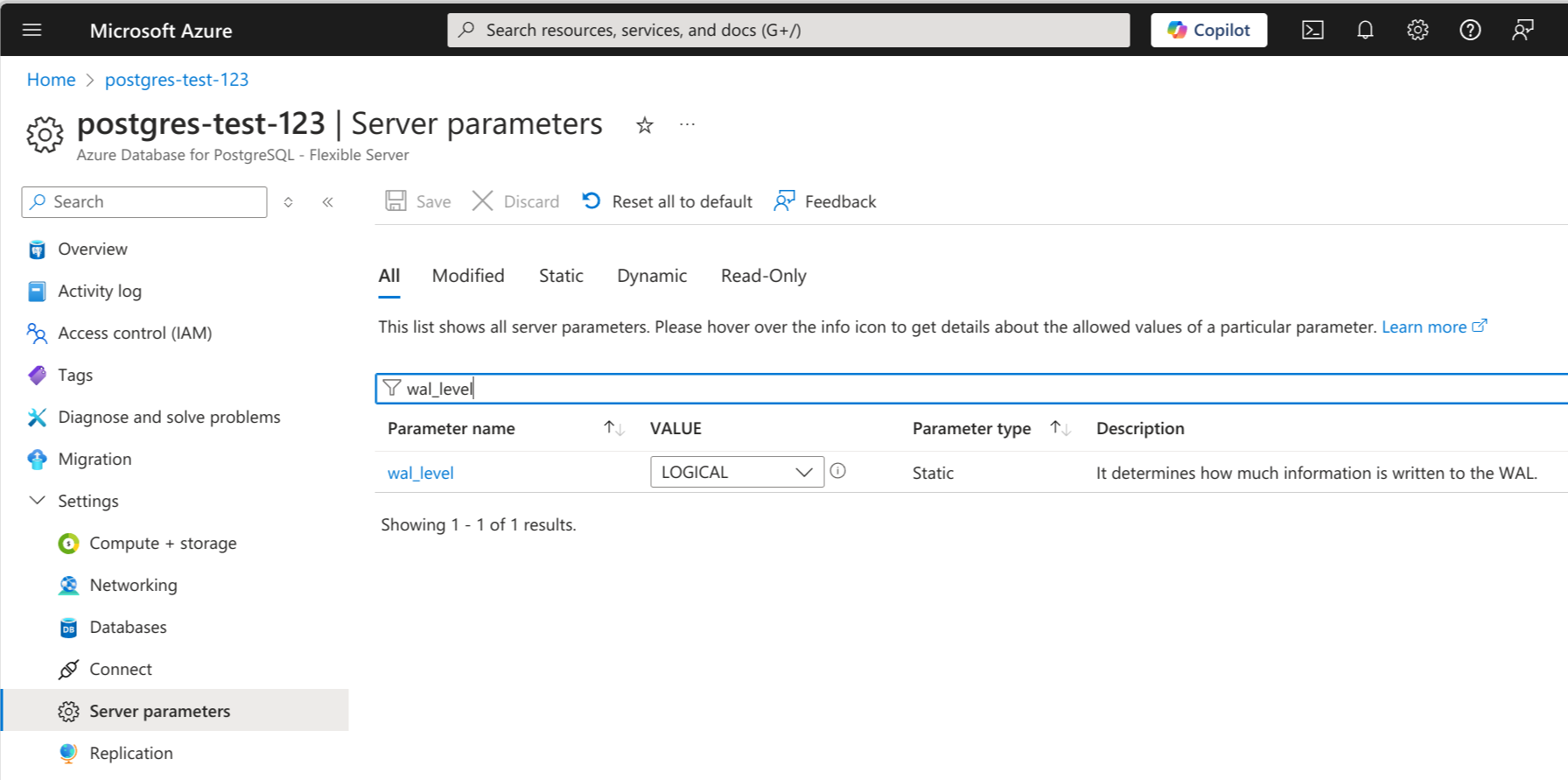
Option 1 - Using Azure Portal:
- Navigate to your PostgreSQL server
- Go to "Server parameters" in the left menu
- Search for "wal_level"
- Change value from "REPLICA" to "LOGICAL"
- Save changes
Option 2 - Using PostgreSQL client:
sql-- Check current wal_level SHOW wal_level; -- Enable logical replication if needed ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = logical; SELECT pg_reload_conf();Grant replication privileges
This must be done using a PostgreSQL client as it cannot be done through Azure Portal:
sqlALTER ROLE username WITH REPLICATION;
Network Access Configuration
In the Azure Portal, select your database server
Navigate to "Networking" in the left menu
Under "Firewall rules" you have several options to add rules:
a. Add current client IP automatically:
- Click "+ Add current client IP address"
- Azure will automatically detect and add your current IP address
- This is the quickest way to allow access from your current location
b. Add specific IP address manually:
- Enter a Firewall rule name
- Specify Start IP address
- Specify End IP address (same as Start IP for single address)
- Click "Save"
c. Add IP range (if needed):
- Click "+ Add 0.0.0.0 - 255.255.255.255" to allow access from any IP
- Note: This is not recommended for production environments
SSL Configuration
TLS/SSL is enforced on Azure Database servers by default. To configure SSL:
Download the global Azure SSL certificate from Microsoft's official documentation
- This certificate works for all Azure Database instances
Configure SSL in DBConvert Streams:
- Enable SSL mode
- Upload the global certificate
- Select "Verify-CA" as SSL mode
:::note TLS/SSL connection is required by default. If you need to disable SSL, you can update the require_secure_transport server parameter to OFF, but this is not recommended for production environments. :::
Connection Setup in DBConvert Streams
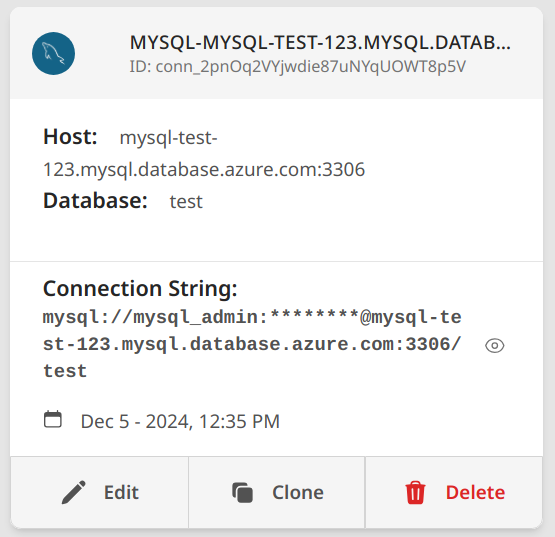
For MySQL Databases
- Select MySQL as database type
- Enter connection details:
- Server:
<servername>.mysql.database.azure.com - Port: 3306
- User ID: Your database username
- Password: Your password
- Database: Your database name
- Server:
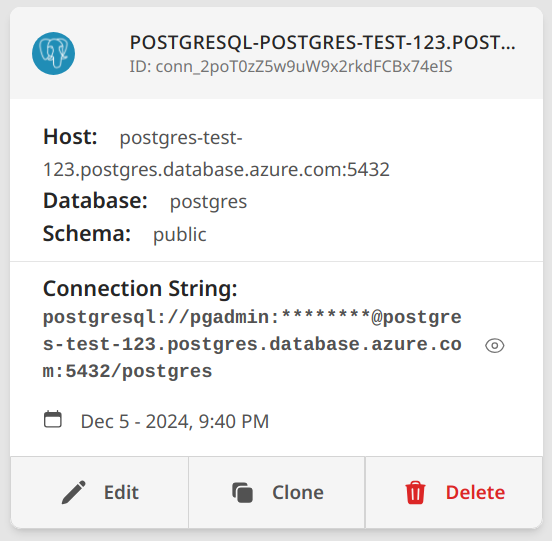
For PostgreSQL Databases
- Select PostgreSQL as database type
- Enter connection details:
- Server:
<servername>.postgres.database.azure.com - Port: 5432
- User ID: Your database username
- Password: Your password
- Database: Your database name
- Schema: Your schema name (default: public)
- Server:
SSL Configuration
- Download the Azure SSL certificate
- In DBConvert Streams:
- Enable SSL mode
- Upload the global certificate
- Select "Verify-CA" as SSL mode
